What is an Embedded System? A Core Definition
An embedded system is a computer system; a combination of a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system.
It is fundamentally a specialized computer, in contrast to a general purpose computer like a PC.
Comparing System Types: From General to Specific
The world of computing can be seen as a spectrum from highly flexible, general purpose machines to highly specialized, single purpose devices.
| FEATURE | GENERAL PURPOSE PC | COMPLEX EMBEDDED SYSTEM (E.G., SMARTPHONE) | SIMPLE EMBEDDED SYSTEM (COURSE FOCUS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Run any application the user wants. | Perform a primary function (e.g., phone calls) while also running a variety of specialized apps. | Perform one specific task reliably and repeatedly. |
| Examples | Desktop PC, Laptop | iPhone, Android Phone, Smartwatch | Arduino, Refrigerator Controller, Car Engine Control Unit (ECU), Electric Toothbrush |
| Software Stack | Hardware Firmware (BIOS/UEFI) OS (Windows/macOS/Linux) Applications | Hardware Firmware OS (iOS/Android) Apps | Hardware Firmware (That's it!) |
| User Interaction | Full keyboard, mouse, large display. Highly interactive. | Touchscreen, voice commands, limited buttons. | Often no direct user interaction. May have a single button or sensor input. |
| Resources | Abundant (e.g., 16+ GB RAM, 1+ TB Storage) | Moderate (e.g., 8 GB RAM, 256 GB Storage) | Highly Constrained (e.g., 2 KB RAM, 32 KB Storage) |
Defining "Firmware": The Soul of the Machine
Definition: Firmware is a specific class of computer software that provides low-level control for a device's specific hardware. It is the program that is "firmly" embedded into the hardware, often stored in non-volatile memory.
Analogy: If hardware is the body and application software (like Word or Chrome) is the clothing you can change, then firmware is the brainstem—it controls the fundamental, unchanging functions of the body.
Key Characteristics:
- Permanence: It resides on the device in permanent memory (Flash, ROM, EEPROM) and persists even when power is off.
- Single Application: In simple embedded systems, the firmware is the one and only application. The device boots up and runs this program, and nothing else, every single time.
- Hardware-Specific: Firmware is written specifically for the hardware it runs on. You cannot take the firmware from a microwave and run it on a toothbrush.
Introduction to Microprocessors
A microprocessor is the brain of a computer, a single chip containing the full central processing unit (CPU). It's a programmable device that processes binary data based on stored instructions.
- Programmable: Its function is determined by software.
- Clock-Driven: Operations are synchronized by a clock signal.
- Register-Based: Uses high-speed internal memory (registers) for data manipulation.
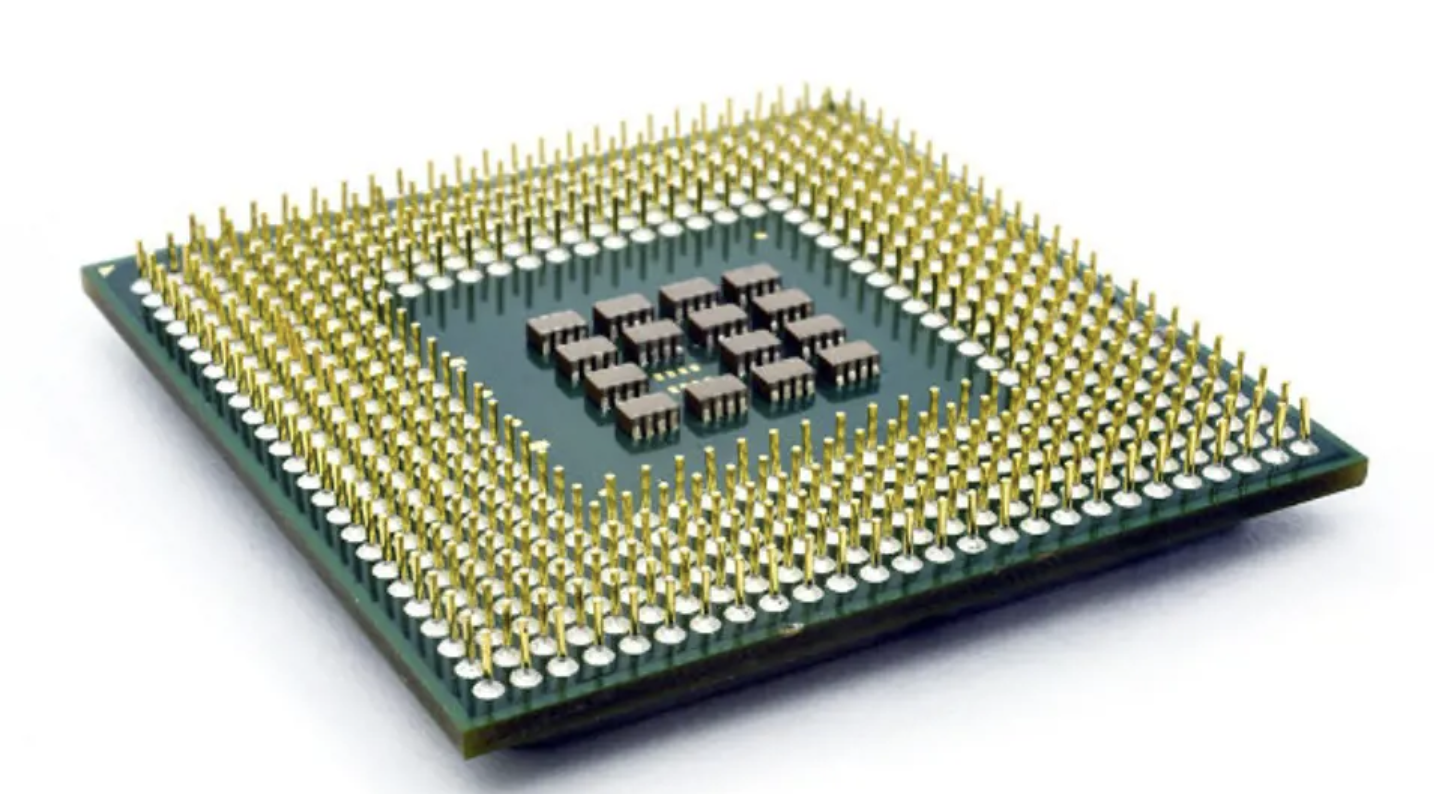
Core Components of a Microprocessor
A microprocessor consists of several key components working together.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs calculations and logical operations.
- Control Unit: Directs the flow of data and instructions.
- Registers: Fast, temporary storage for data and instructions.
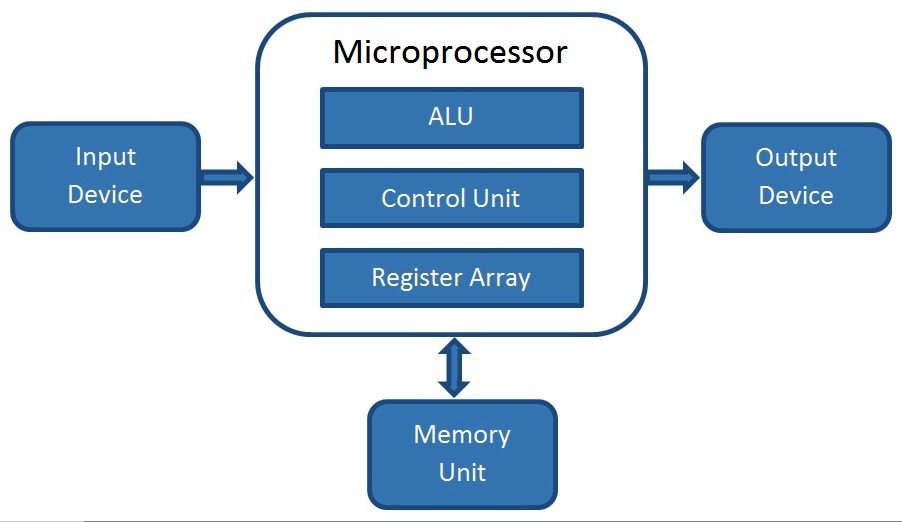
The Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
This is the fundamental process of a microprocessor:
- Fetch: The Program Counter (PC) provides the address of the next instruction. This address is sent to the Memory Address Register (MAR). The instruction at this address is then fetched from memory and stored in the Instruction Register (IR).
- Decode: The Control Unit (CU) interprets the instruction in the IR. It determines the operation to be performed and the data required.
- Execute: The CU sends signals to the appropriate components, such as the ALU and registers, to perform the operation. The result is stored in a register or memory, and the PC is updated to point to the next instruction.
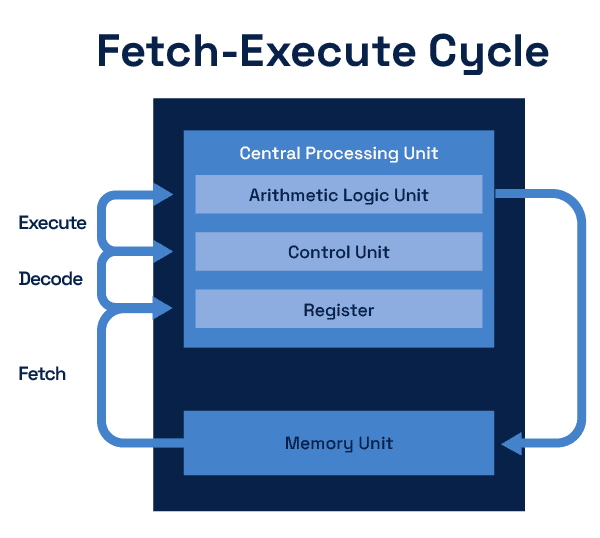
Buses: The Data Highways
Buses are the communication pathways in a computer system.
- Address Bus: Specifies the memory location to access.
- Data Bus: Carries data between the CPU and memory.
- Control Bus: Transmits control signals.
A Brief History of Microprocessors
From humble beginnings to modern powerhouses.
- 1971: Intel 4004 - The first commercial microprocessor.
- 1978: Intel 8086 - The start of the x86 architecture.
- Present: Multi-core, 64-bit processors with billions of transistors.
The 8085 Microprocessor: A Classic Example
The Intel 8085 is a foundational 8-bit microprocessor.
- 8-bit data bus, 16-bit address bus
- Can address 64 KB of memory
- Used in many early computer systems and for education.
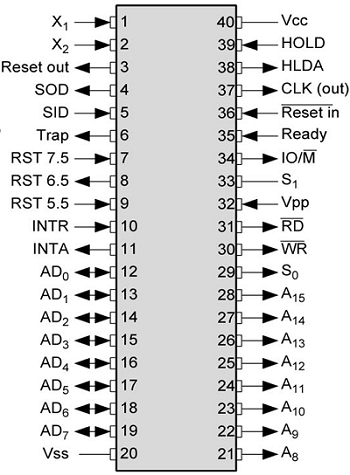
8085 Architecture
A closer look at the internal structure of the 8085.
- General-purpose and special-purpose registers
- A rich instruction set for various operations
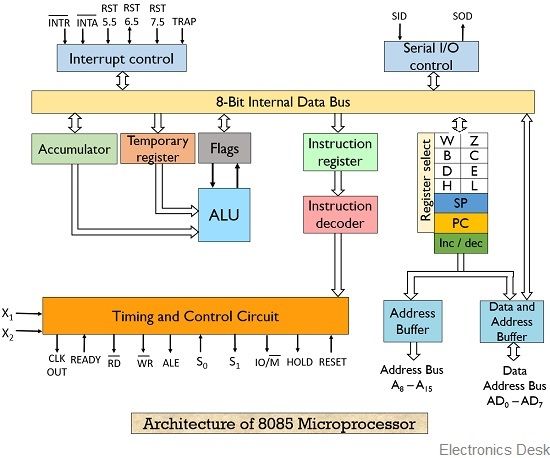
Memory and I/O Interfacing
How the CPU communicates with the outside world.
- Memory-Mapped I/O: I/O devices are treated like memory locations.
- Isolated I/O: Separate address spaces for memory and I/O.
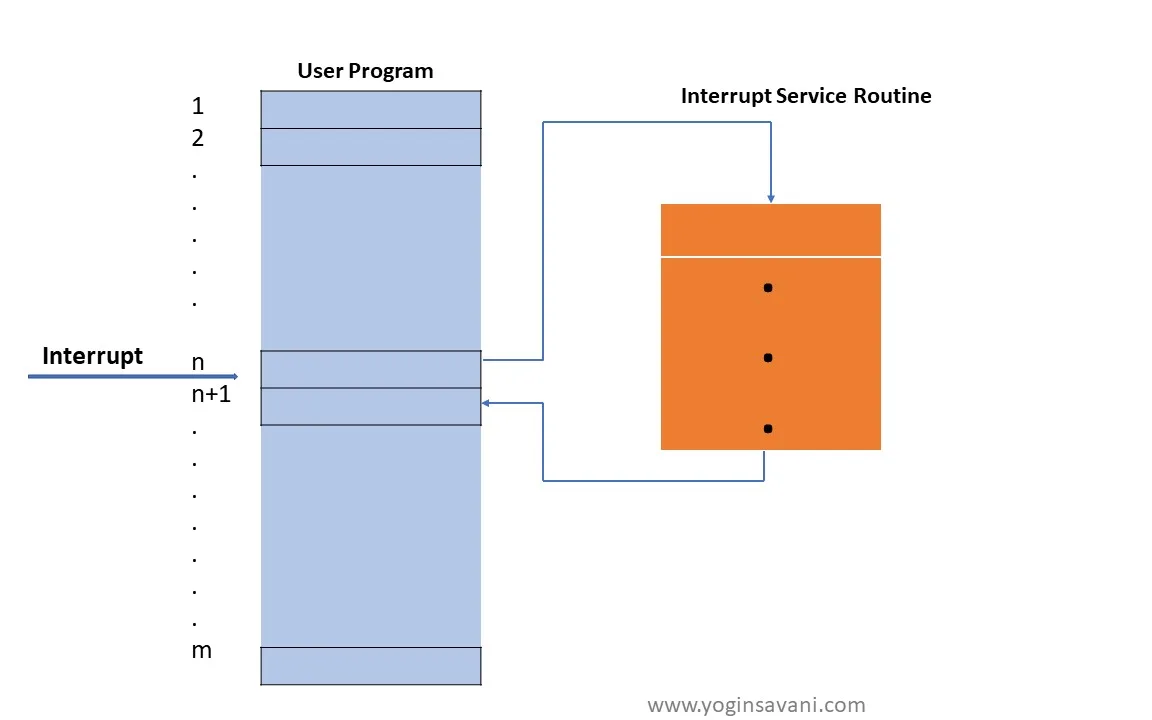
Interrupts
A mechanism for hardware or software to request the CPU's attention.
- Allows for efficient handling of asynchronous events.
- The CPU suspends its current task, services the interrupt, and then resumes.
Conclusion (Microprocessors)
Microprocessors are the foundation of modern computing. Understanding their architecture and operation is key to understanding how computers work.
Case Study: The MOS Technology 6502
An iconic microprocessor that powered a generation of computers and game consoles.
- Simple, elegant design
- Used in the Apple II, Commodore 64, and Nintendo Entertainment System
6502 in Action
The 6502 was at the heart of many revolutionary products.

6502 Architecture
A look at the registers and internal structure of the 6502.
- Accumulator, index registers, program counter, stack pointer
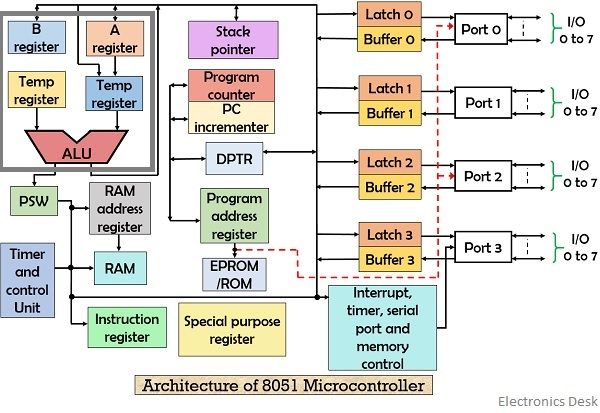
Microcontroller Case Study: The Intel 8051
The 8051 is a classic 8-bit microcontroller that is still popular for learning and in many embedded systems.
- CPU: 8-bit CPU optimized for control applications.
- Memory: Separate memory spaces for program (ROM) and data (RAM).
- I/O: Four 8-bit I/O ports for interfacing with other devices.
- Timers/Counters: Two 16-bit timers/counters.
- Serial Port: For serial communication.
Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
A microcontroller is a computer on a chip.
- Microprocessor: Just the CPU.
- Microcontroller: CPU + Memory + Peripherals.
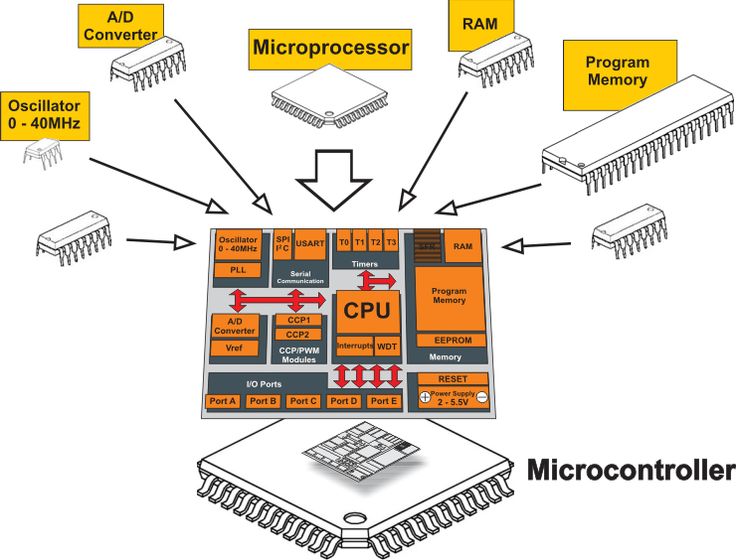
Inside a Microcontroller
A microcontroller integrates many components into a single package.
- RAM, ROM/Flash, GPIO, Timers, UART, SPI, I2C, ADC, DAC
The Landscape of Microcontroller Design
Model 1: The Vertically Integrated (Proprietary) Model
A single company controls the entire stack: CPU design, peripheral integration, chip manufacturing, and sales. This creates a self-contained ecosystem with proprietary tools and architectures.
- Microchip PIC: A cornerstone of the 8/16-bit world, known for robustness. Uses MPLAB X IDE.
- Atmel AVR: A highly efficient 8-bit RISC-like architecture, famous for being the core of Arduino.

The Landscape of Microcontroller Design
Model 2: The ARM Ecosystem (IP Licensing)
ARM designs processor cores and licenses them to other companies. These companies then build unique microcontrollers around the licensed core.
- ARM: The "Engine Designer" (e.g., Cortex-M series).
- Semiconductor Companies (e.g., ST, NXP, TI): The "Car Manufacturers" who add peripherals, memory, and special features.
- Benefit: Skill portability for engineers and a diverse market of application-specific chips.




The Programming Hierarchy
Most embedded systems are programmed in high-level languages like C and C++, which offer portability and readability. However, low-level programming is still essential.
Why Use Assembly?
- Direct Hardware Control: To manipulate specific hardware registers that are not accessible from C.
- Performance Optimization: Hand-crafting assembly for critical loops can be smaller and faster than compiler-generated code.
- Bootloaders & Startup Code: The very first code a processor runs after power-on is often in assembly to set up the system before C code can run.
- Extreme Constraints: On tiny microcontrollers with very limited memory, every byte counts.
Conclusion (Microcontrollers)
Microcontrollers are at the heart of the vast world of embedded systems, from everyday appliances to complex industrial machinery.