MF52A Thermistor
Arduino Workshop
What is the MF52A Sensor?
The MF52A is a thermistor - a type of resistor whose resistance changes with temperature.
- NTC Type: Negative Temperature Coefficient - resistance decreases as temperature increases
- Resistance at 25°C: Typically 10kΩ (10,000 ohms)
- Temperature Range: -55°C to +125°C
- Applications: Room temperature monitoring, weather stations, HVAC systems
How Does a Thermistor Work?
A thermistor's resistance changes predictably with temperature:
- Cold Environment: High resistance (more opposition to current flow)
- Hot Environment: Low resistance (less opposition to current flow)
By measuring the resistance, we can calculate the temperature using the Steinhart-Hart equation or a simplified B-parameter equation.
Key Point: Arduino can't measure resistance directly - it measures voltage. We'll use a voltage divider circuit!
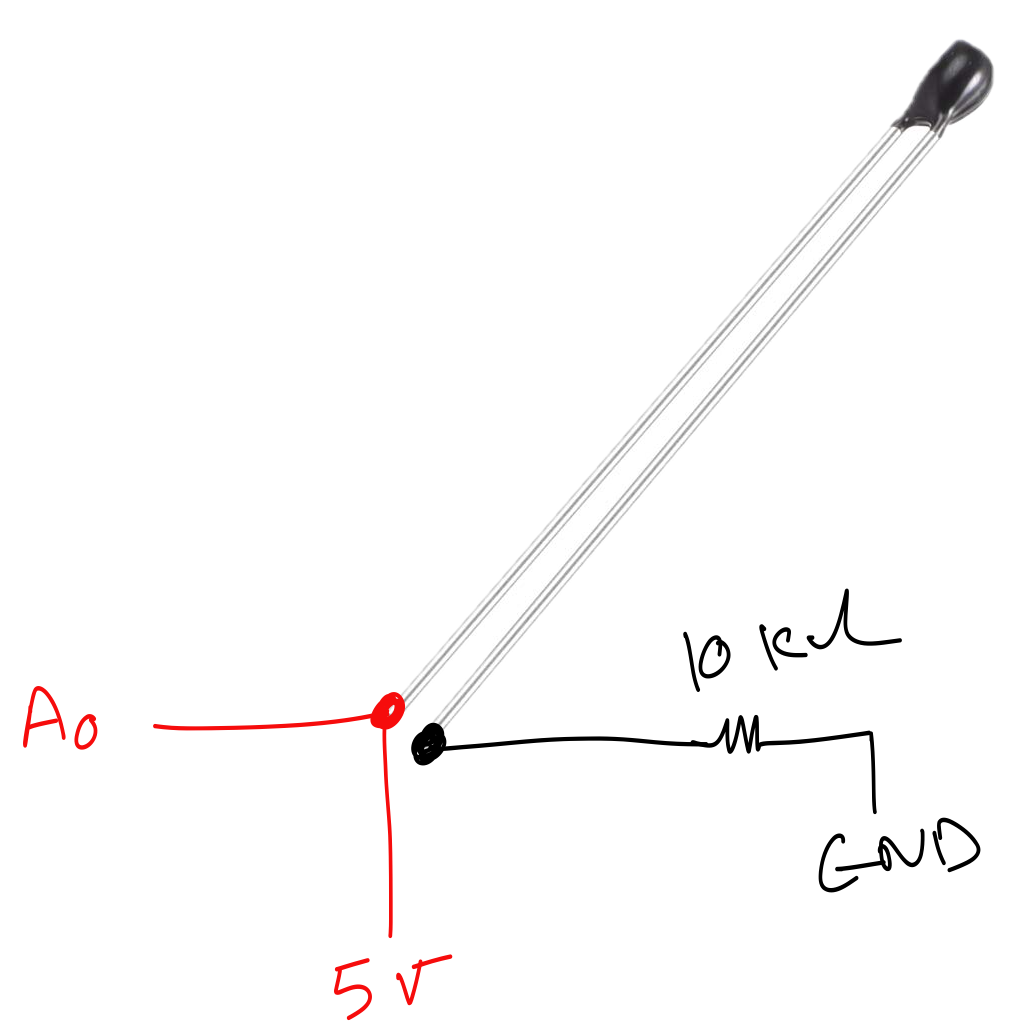
Wiring the MF52A to Arduino
We'll create a voltage divider circuit with two resistors:
- Component 1: MF52A thermistor (variable resistance)
- Component 2: 10kΩ fixed resistor
Connections:
- 5V → Thermistor → A0 (analog pin) → 10kΩ resistor → GND
- The middle connection (between thermistor and fixed resistor) goes to analog pin A0
This circuit converts changing resistance into changing voltage that Arduino can read!